Passivation is the process of removing free iron from the surface of stainless steel. During the manufacturing process, free iron is incorporated into the surface of the part during various stages of machining, deburring, etc. The free iron on the surface can then form a visible rust on the surface of the part. Historically passivation was performed using nitric acid as opposed to citric acid. Citric was avoided because due to propensity of organic growth of bacteria and mold to contaminate the bath. Recent advances in formulations have overcome these biological contaminate buildups and have made citric acid a popular choice in a wide range of industries. The advantages of citric versus nitric passivation are many and have made passivation accessible to companies with little or no experience in chemical processing and handling.
The first and foremost benefit of using citric acid rather than nitric acid is the safety factor for both workers and the environment. Citric acid is non-fuming, non-toxic, and biodegradable. Secondly, the process itself can be less expensive due to lower operating concentrations, shorter production times, and less environmental/WWT concerns. Lastly, citric passivation only removes iron from the surface without affecting the other metals contained in the different alloys. Citric has been found to have excellent results on all grades of stainless while meeting most current industry standard.
BroCo 539M is a citric based acid product used in brightening, cleaning, activating and passivating applications. Our products versatile use has made it one of our most popular products. At 30% v/v BroCo 539M meets ASTM A967, section 7.1, Paragraph 7.1.1.1-7.1.1.4 Citric 1- Citric 4. Alternatively we offer straight citric blends with no added components to make an extremely economical alternative.
From ASTM A967-05 Section 7. Treatments in Citric Acid
7.1 Passivation Treatment:
7.1.1 Stainless steel parts shall be treated in one of the following aqueous solutions and maintained within the specified temperature range for the specified time.
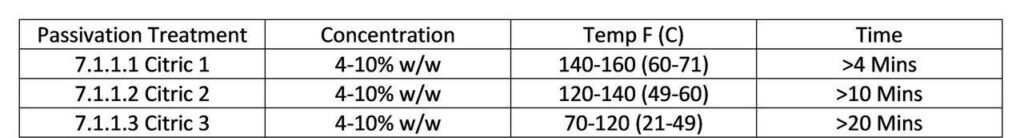
7.1.1.1 Citric 1—The solution shall contain 4 to 10 weight percent of citric acid. The parts shall be immersed for a minimum of 4 min at a temperature in the range from 140 to 160°F (60 to 71°C).
7.1.1.2 Citric 2—The solution shall contain 4 to 10 weight percent of citric acid. The parts shall be immersed for a minimum of 10 min at a temperature in the range from 120 to 140°F (49 to 60°C).
7.1.1.3 Citric 3—The solution shall contain 4 to 10 weight percent of citric acid. The parts shall be immersed for a minimum of 20 min at a temperature in the range from 70 to 120°F (21 to 49°C).
7.1.1.4 Citric 4—Other combinations of temperature, time, and concentration of citric acid, with or without other chemicals to enhance cleaning, including accelerants, inhibitors, or proprietary solutions capable of producing parts that pass the specified test requirements.
7.1.1.5 Citric 5—Other combinations of temperature, time, and concentrations of citric acid, with or without other chemicals to enhance cleaning, including accelerants, inhibitors, or proprietary solutions capable of producing parts that pass the specified test require
7.2 Water Rinse—Immediately after removal from the passivating solution, the parts shall be thoroughly rinsed, using stagnant, countercurrent, or spray washes, singly or in combination, with or without a separate chemical treatment for neutralization of the passivation media (see 9.2), with a final rinse being carried out using water with a maximum total solids content of 200 ppm.
